

O zinco é um micronutriente que
compõe mais de 300 enzimas envolvidas
em funções importantes para o
desempenho físico, como produção de
energia muscular e síntese de proteínas.
É também essencial para a produção de
testosterona e responsável pelo
bloqueio da enzima aromatase, que
transforma o excesso de testosterona
em estrogênio. Também tem poder
antioxidante e fortalece o sistema
imunológico, reduzindo o risco de
infecções. A deficiência grave de zinco
resulta em sintomas como dermatite
pustular, alopécia, perda de peso, diarréia,
infecções secundárias à disfunção
imunológica, hipogonadismo e
problemas na cicatrização de úlceras.
É necessário para a formação da estrutura da pele, para
a proliferação celular e para manter a integridade de
membranas, síntese de ácidos nucleicos e a síntese de
colágeno. Na deficiência de zinco, a produção de
fibroblastos e colágeno é reduzida.
A suplementação de zinco tem o potencial de melhorar
a imunidade. Em idosos, com baixa concentração sérica
de zinco, foram investigados os efeitos da
suplementação por 3 meses.3
Os autores do trabalho
concluíram que a suplementação de zinco em idosos e
seu consequente aumento sérico, foram associados ao
aprimoramento da função das células T. Baixos níveis
séricos de zinco também estão associados à
encefalopatia hepática. Um estudo teve como objetivo
investigar os efeitos da suplementação de zinco no
tratamento de encefalopatia hepática em pacientes
com cirrose. Quatro ensaios clínicos com 247 pacientes
foram incluídos.
Em conclusão, uma combinação de suplementação de
zinco e lactulose por 3 a 6 meses melhorou o teste de
conexão numérica em pacientes cirróticos com
encefalopatia hepática de baixo grau, em comparação
com apenas lactulose.
Um outro trabalho investigou os efeitos da
suplementação oral de zinco sobre a intensidade da
fadiga e a qualidade de vida de pacientes durante a
quimioterapia para neoplasia colorretal. Foi constatado
que a suplementação com zinco previne a fadiga e
preserva a qualidade de vida de pacientes em
quimioterapia para neoplasia colorretal.5
Outros autores
avaliaram os efeitos da suplementação de zinco no
controle glicêmico, parâmetros cardiometabólicos e
antropométricos e a progressão da doença em
pré-diabetes. A suplementação com zinco reduziu a
resistência à glicose no sangue e à insulina, melhorando a
função das células β. Além disso, a suplementação
reduziu a progressão da doença para o diabetes e teve
efeitos benéficos no colesterol total e no LDL-C.
O zinco, assim como outros micronutrientes, é
conhecido por exercer vários efeitos benéficos ao
organismo, incluindo ações antiinflamatórias e
antioxidantes. Alguns trabalhos evidenciam que a
suplementação de zinco pode melhorar parâmetros
bioquímicos de inflamação como a proteía C reativa,
expressão gênica de IL-1 e TNF-α.

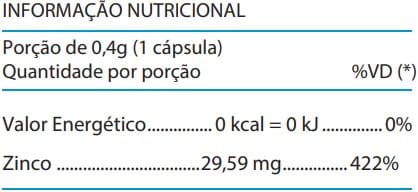
Recomenda-se a ingestão de 1 (uma) cápsula ao dia, para adultos acima de 19 anos.
ARMAZENAMENTO: Conservar ao abrigo da luz, umidade e
calor excessivo e com embalagem fechada, inclusive após
aberto. Não consumir este produto caso o lacre de
segurança esteja violado.
NÃO EXCEDER A RECOMENDAÇÃO DIÁRIA DE CONSUMO INDICADA NA EMBALAGEM.
ESTE PRODUTO NÃO É UM MEDICAMENTO. MANTENHA FORA DO ALCANCE DE CRIANÇAS.

Bisglicinato de Zinco (Zinco) e Veículo (Óleo de Soja); Cápsula: Água Purificada, Geleificante (Gelatina), Umectante (INS 422) e Corantes (INS 171 e INS 133). NÃO CONTÉM GLÚTEN. ALÉRGICOS: CONTÉM DERIVADOS DE SOJA.

1. Zinc Is the Most Important Trace
Element.
2. Hair, Nails, and Skin: Differentiating
Cutaneous Manifestations of
Micronutrient Deficiency.
3. Effect of Zinc Supplementation on
Serum Zinc Concentration and T Cell
Proliferation in Nursing Home Elderly: A
Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-
-Controlled Trial.
4. Zinc Supplementation in Patients With
Cirrhosis and Hepatic Encephalopathy: A
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
5. Effects of Zinc Supplementation on
Fatigue and Quality of Life in Patients With
Colorectal Cancer.
6. Zinc Supplementation in Prediabetes: A
Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial.
7. Zinc supplementation improves
glycemic control for diabetes prevention
and management: a systematic review
and meta-analysis of randomized
controlled trials.
8. The Effects of Magnesium and Zinc
Co-Supplementation on Biomarkers of
Inflammation and Oxidative Stress, and
Gene Expression Related to Inflammation
in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: a
Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial.
9. The effect of zinc supplementation on
plasma C-reactive protein concentrations:
A systematic review and meta-analysis of
randomized controlled trials.
*- Role of vitamins D, E and C in immunity
and inflammation
- Vitamin D and Immune Function.
- Regulatory role of vitamin E in the
immune system and inflammation
- Effect of Selenium Supplementation on
Antioxidant Markers: A Systematic Review
and Meta-Analysis of Randomized
Controlled Trials.
- The role of selenium in inflammation and
immunity: from molecular mechanisms to
therapeutic opportunities.
- Vitamin A and vitamin D regulate the
microbial complexity, barrier function, and
the mucosal immune responses to
ensure intestinal homeostasis.
- Vitamin A, infection, and immune
function.
- The effect of zinc supplementation on
plasma C-reactive protein concentrations:
A systematic review and meta-analysis of
randomized controlled trials.
- Extra Dose of Vitamin C Based on a Daily
Supplementation Shortens the Common
Cold: A Meta-Analysis of 9 Randomized
Controlled Trials.